what should sugar levels be for gestational diabetes Pre-existing diabetes and pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is important for women to maintain a healthy lifestyle and take extra care of their bodies. For those who have pre-existing diabetes, additional precautions and considerations need to be taken to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy. Similarly, women diagnosed with gestational diabetes during pregnancy also need to manage their condition effectively. In this post, I will discuss both pre-existing diabetes and gestational diabetes, along with tips on how to deal with them during pregnancy. Pre-existing Diabetes and Pregnancy: Women who have diabetes before becoming pregnant fall under the category of pre-existing diabetes. This can be either type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Managing diabetes during pregnancy requires careful blood sugar level monitoring and adjustments in insulin or oral medications as prescribed by the healthcare provider. The target blood sugar levels for pregnant women with pre-existing diabetes may be different from those without diabetes. 
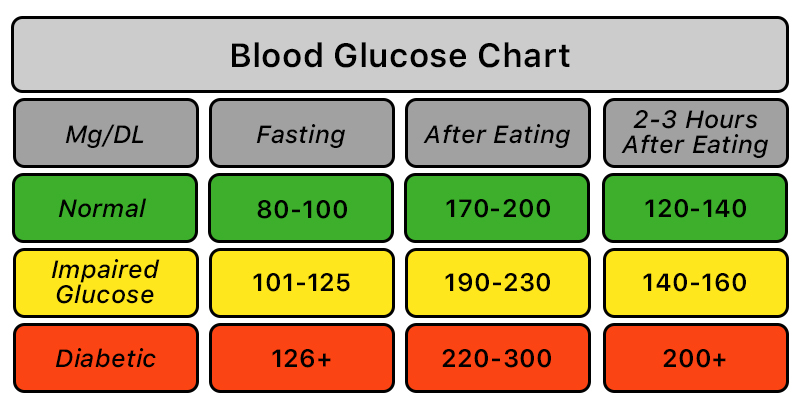
Target Blood Sugar Levels
During pregnancy, the target blood sugar levels for women with pre-existing diabetes are generally lower than those without diabetes. The American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets:
- Fasting blood sugar: less than 95 mg/dL
- 1 hour after a meal: less than 140 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: less than 120 mg/dL
It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the specific target levels based on your individual needs.
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for both the health of the mother and the unborn baby. High blood sugar levels during pregnancy can increase the risk of complications such as preeclampsia, premature birth, and birth defects. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels can lead to hypoglycemia, which can be dangerous for both the mother and baby.
In addition to close monitoring of blood sugar levels, women with pre-existing diabetes should also focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle throughout pregnancy. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity as advised by the healthcare provider, and taking prescribed medications or insulin as required.
How to Deal with Gestational Diabetes during Pregnancy
Gestational diabetes is a condition that develops during pregnancy and affects the way the body uses insulin. It typically occurs around the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy and disappears after giving birth. However, women diagnosed with gestational diabetes need to manage their condition and keep their blood sugar levels under control for the well-being of both themselves and their unborn baby.  Managing gestational diabetes involves making lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and regular exercise. Here are some important tips to deal with gestational diabetes during pregnancy:
Managing gestational diabetes involves making lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and regular exercise. Here are some important tips to deal with gestational diabetes during pregnancy:
- Follow a well-balanced diet: Focus on eating foods that are rich in fiber, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid or limit refined carbohydrates and sugary foods.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly check your blood sugar levels as directed by your healthcare provider. Keep a record of your levels and make any necessary adjustments to your diet or medications.
- Stay active: Engage in moderate physical activity, such as walking or swimming, as advised by your healthcare provider. Exercising regularly can help control blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Take prescribed medications: If lifestyle modifications alone are not enough to keep blood sugar levels under control, your healthcare provider may prescribe medication or insulin to manage gestational diabetes.
- Attend regular prenatal check-ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider are important to monitor the development of your baby and ensure that your gestational diabetes is well-managed.
It’s important to remember that gestational diabetes can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. However, with proper management and adherence to the recommended lifestyle changes, most women with gestational diabetes deliver healthy babies.
In conclusion, both pre-existing diabetes and gestational diabetes require careful management during pregnancy. By closely monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and taking prescribed medications as advised, women can successfully manage these conditions and have a safe and healthy pregnancy. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support throughout your pregnancy journey. If you are looking for Blood Sugar Chart | What is Normal Blood Glucose? | Lark Health you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Images about Blood Sugar Chart | What is Normal Blood Glucose? | Lark Health like Blood Sugar Chart | What is Normal Blood Glucose? | Lark Health, Pre-existing Diabetes And Pregnancy and also How to Deal with Gestational Diabetes during Pregnancy | Top 10 Home. Read more:
Blood Sugar Chart | What Is Normal Blood Glucose? | Lark Health
 www.lark.comsugar glucose lark levels fasting
www.lark.comsugar glucose lark levels fasting
Blood Sugar Levels For Pregnant Women With Diabetes | For The Future
 www.pinterest.comblood sugar pregnancy diabetes levels pregnant glucose normal chart level high during gestational test fasting hour range type average when
www.pinterest.comblood sugar pregnancy diabetes levels pregnant glucose normal chart level high during gestational test fasting hour range type average when
How To Deal With Gestational Diabetes During Pregnancy | Top 10 Home
 www.top10homeremedies.comdiabetes gestational pregnancy during sugar levels deal symptoms blood treatment causes risk reduce pregnant manage problem type eat factors lower
www.top10homeremedies.comdiabetes gestational pregnancy during sugar levels deal symptoms blood treatment causes risk reduce pregnant manage problem type eat factors lower
Pin On Diabetes Information
 www.pinterest.comPre-existing Diabetes And Pregnancy
www.pinterest.comPre-existing Diabetes And Pregnancy
 www.thediabetescouncil.compregnancy sugar blood levels diabetes pregnant during target pre existing monitoring
www.thediabetescouncil.compregnancy sugar blood levels diabetes pregnant during target pre existing monitoring
Blood sugar pregnancy diabetes levels pregnant glucose normal chart level high during gestational test fasting hour range type average when. Blood sugar levels for pregnant women with diabetes. Pregnancy sugar blood levels diabetes pregnant during target pre existing monitoring